Mitosis and meiosis are two important processes in cell division that play crucial roles in the growth and reproduction of organisms. While both processes involve the division of cells, they differ in their purpose and outcomes.
During mitosis, a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. This process is essential for growth, repair, and asexual reproduction in organisms.
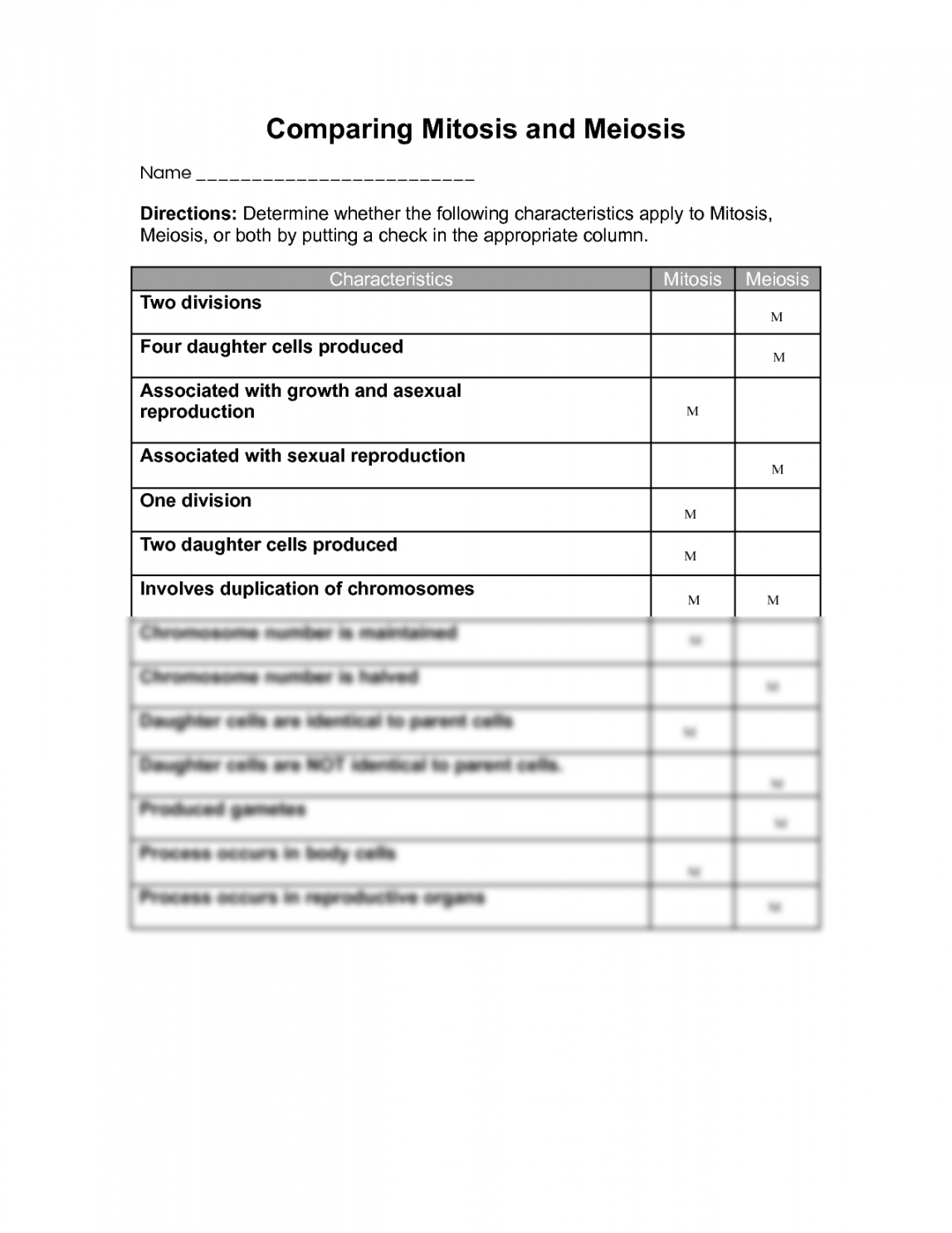
Worksheet Comparing Mitosis and Meiosis
1. Number of divisions:
– Mitosis: One division
– Meiosis: Two divisions
2. Purpose:
– Mitosis: Growth, repair, asexual reproduction
– Meiosis: Sexual reproduction, genetic diversity
3. Daughter cells produced:
– Mitosis: Two identical daughter cells
– Meiosis: Four genetically diverse daughter cells
4. Chromosome number:
– Mitosis: Same as parent cell
– Meiosis: Half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell
5. Occurs in:
– Mitosis: Somatic cells
– Meiosis: Germ cells
In conclusion, while mitosis and meiosis both involve cell division, they serve different purposes and produce different outcomes. Mitosis is essential for growth and repair, while meiosis is crucial for sexual reproduction and genetic diversity in organisms.