Elements, compounds, and mixtures are the building blocks of chemistry. Understanding the differences between these three types of substances is essential in the study of matter and its properties. Each plays a unique role in the composition and behavior of materials around us.
Elements are pure substances made up of only one type of atom. They cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. The periodic table of elements lists all known elements, each with its own unique properties and atomic number. Examples of elements include oxygen, carbon, and iron.
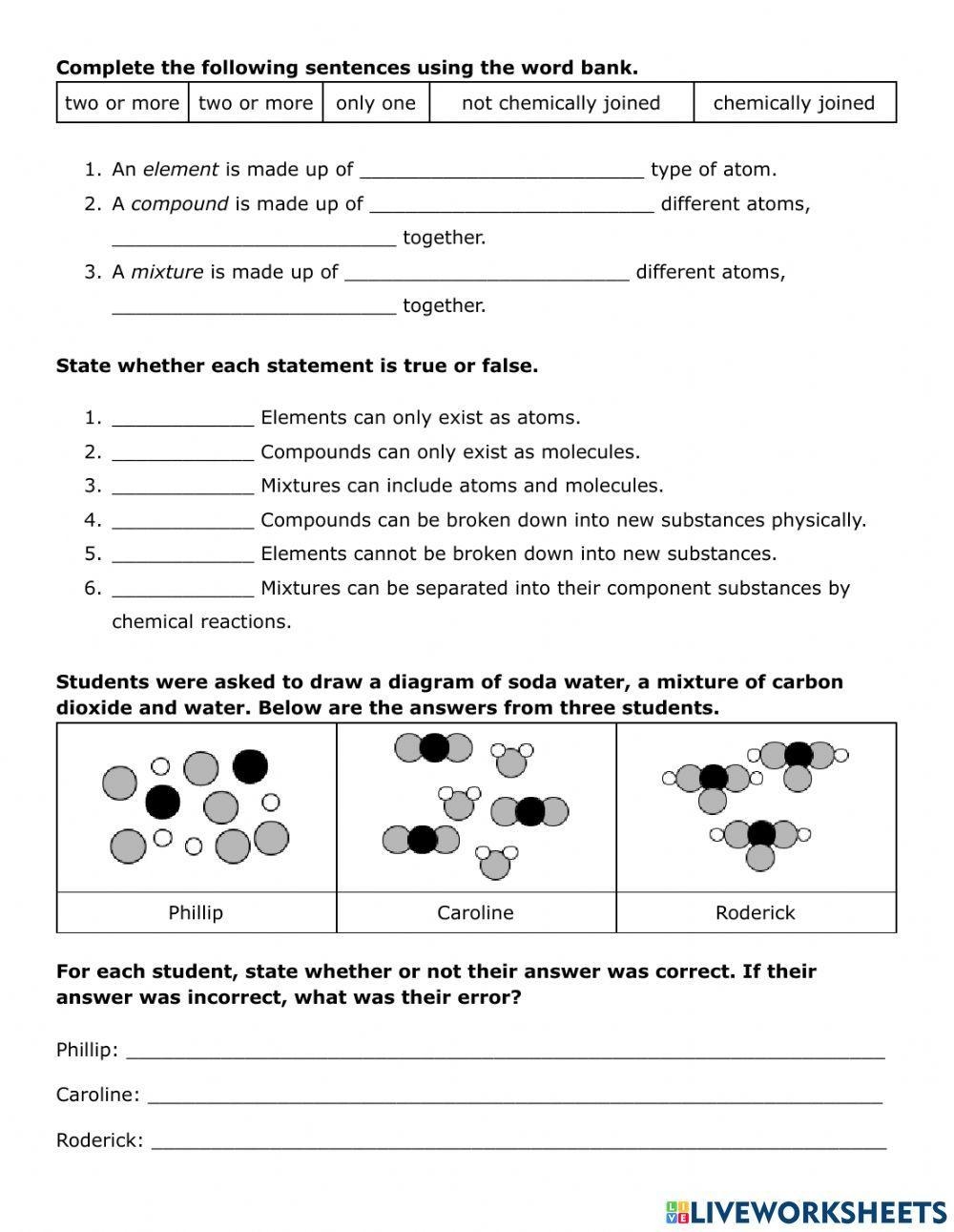
Worksheet: Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures
Compounds, on the other hand, are substances made up of two or more elements chemically combined in fixed proportions. The atoms in compounds are held together by chemical bonds, creating new substances with distinct properties. Water (H2O) and carbon dioxide (CO2) are examples of compounds.
Mixtures, unlike compounds, are combinations of two or more substances that are physically mixed together but not chemically bonded. Mixtures can be homogeneous (uniform composition) or heterogeneous (non-uniform composition). Examples of mixtures include saltwater (homogeneous) and trail mix (heterogeneous).
Identifying whether a substance is an element, compound, or mixture is crucial in analyzing its properties and behavior. This knowledge helps scientists predict how substances will interact with each other and how they can be separated or combined in various processes.
By completing worksheets that focus on elements, compounds, and mixtures, students can practice distinguishing between these fundamental concepts and deepen their understanding of chemistry. These exercises typically involve identifying substances, classifying them into the correct category, and explaining the differences between elements, compounds, and mixtures.
In conclusion, elements, compounds, and mixtures are essential components of the study of chemistry. Each plays a distinct role in the composition and behavior of matter. By learning to differentiate between these types of substances, students can gain a better understanding of the world around them and the interactions that occur between different materials.